This is the basic theorem of similarities.
The Tales' theorem says: If two straight lines, not necessarily parallel, are cut by a system of parallel lines, then the resultant segments on one of the two lines are proportional to the respective segments obtained on the other line.
A figure to illustrate the above statement:
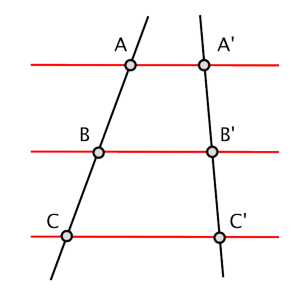
it is satisfied that
Example
For example, given the following figure, decide whether the resultant segments are similar or not.
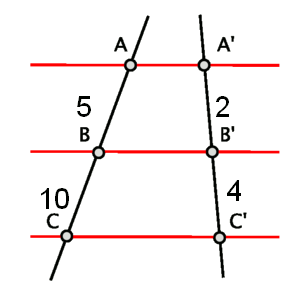
As we can see in the figure, the segment lengths are as follows:
Finally, we give an application that can be useful for solving certain exercises. Thanks to Tales' Theorem, we can calculate the height of an object, for example, a tree, by the following mechanism.
- Let
- Let
- Let
Then, it is satisfied that the height of the tree, called
