The area of the regular polygon is
The perimeter is:
with
Example
Calculate the area of a hexagon of
- Using Pythagoras we find the apothem
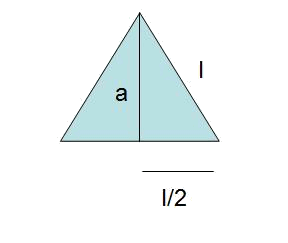
-
The area of one of the triangles:
- Finally, multiplying by
Note: To find areas of more complex irregular polygons, the philosophy will be the same: to break them down into triangles and to add the areas of the triangles.
