The sine function,
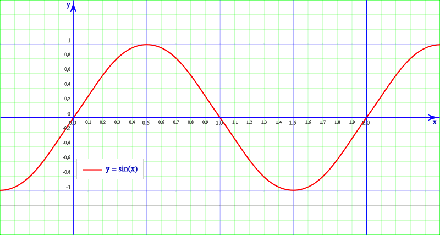
- Domain:
- Image:
- Period:
- Continuity: It is continuous on
- Increasing on:
- Decreasing on:
- Maxima at:
- Minima at:
- Parity: Odd,
- Points of intersection with the axis Ox:
The cosine function,
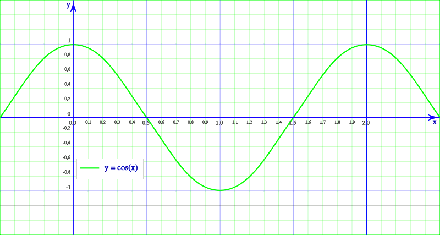
- Domain:
- Image:
- Period:
- Continuity: It is continuous on
- Increasing on:
- Decreasing on:
- Maxima at:
- Minima at:
- Parity: Pair
- Points of intersection with the axis Ox:
The tangent function,
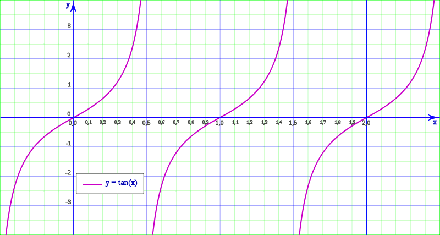
- Domain:
- Image:
- Period:
- Continuity: It is continuous on
- Increasing on:
- Maxima: No maxima
- Minima: No minima
- Parity: Odd
- Points of intersection with the axis Ox:
