Constant function
This is a function of the type
This way, for instance, if we wanted to represent a quantity that stays constant over the course of time
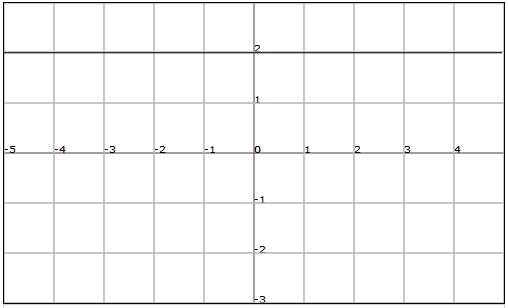
The constant functions cut through the vertical axis in the value of the constant and they are parallel to the horizontal axis (and therefore they do not cut through it).
The graph of a constant function, for example
Linear function
The function of a real variable that takes as a general equation
In the linear functions of this type (
Example
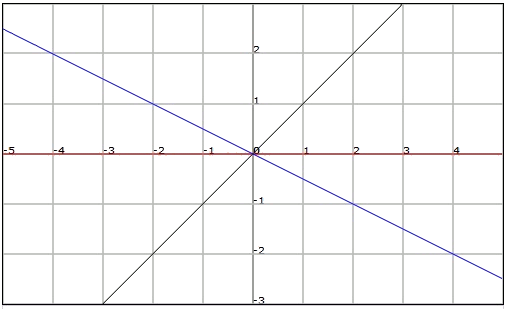
The slope of the straight line
The slope of the straight line
The slope of the straight line
It is important to understand that the larger the value of the slope
-
If
-
If
- If
The slope of a line can also be calculated using the coordinates of a point of the line for a linear function, and from the coordinates of two points for any line.
Let's see the general way since it will also serve us well for the affine functions:
Given two points of a line (be it a linear or affine function)
Example
Considering the following line that passes through point
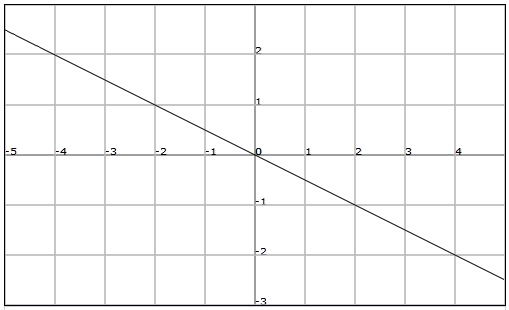
we can calculate the slope, since in addition to point
Affine function
The function of a real variable that takes as a general equation
As in the previous case,
It is also worth mentioning that the cutting point of an affine function
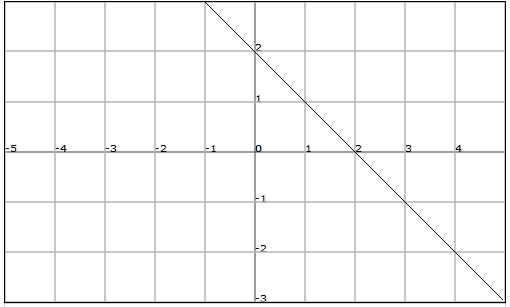
Example
An example of affine function is
Example
Consider the following functions, and determine of which type they are, at what point they cut through the axis of ordinates, and the abscissa, and what their slopes are.
-
- This is a constant function. Its slope is
- This is a linear function. Its slope is
- This is an affine function. Its slope is

